Functions and measurement routines
This page provides a brief overview of some functions and measuring routines of our Triboster TSf-503.
For more detailed information, please Contact Us or your local agent. "Where To Buy"
Automatic contact probe lift-up function
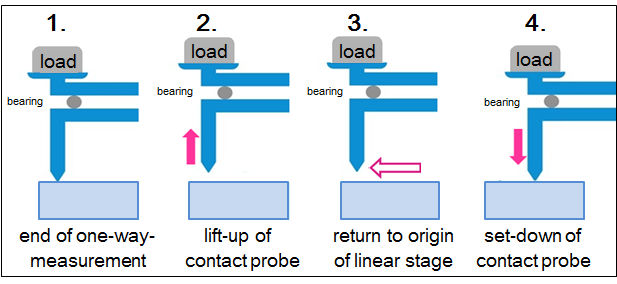
Continuous static friction
Used for measurements focusing on static friction, generally measured with slow speeds up to 1.0mm/s.
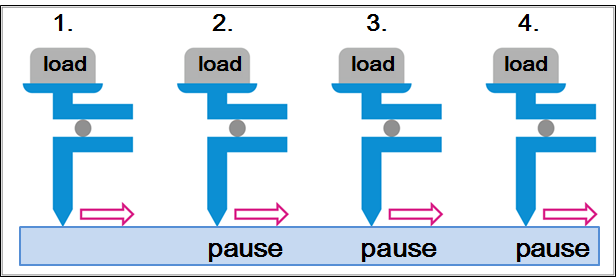
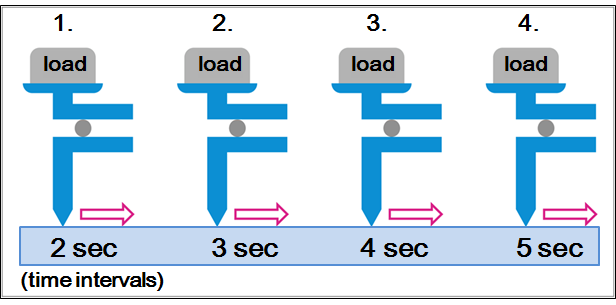
Time-interval dependency
Used to evaluate the influence of adhesion between the sample and the contact probe or attached specimen.